 Overview
Overview

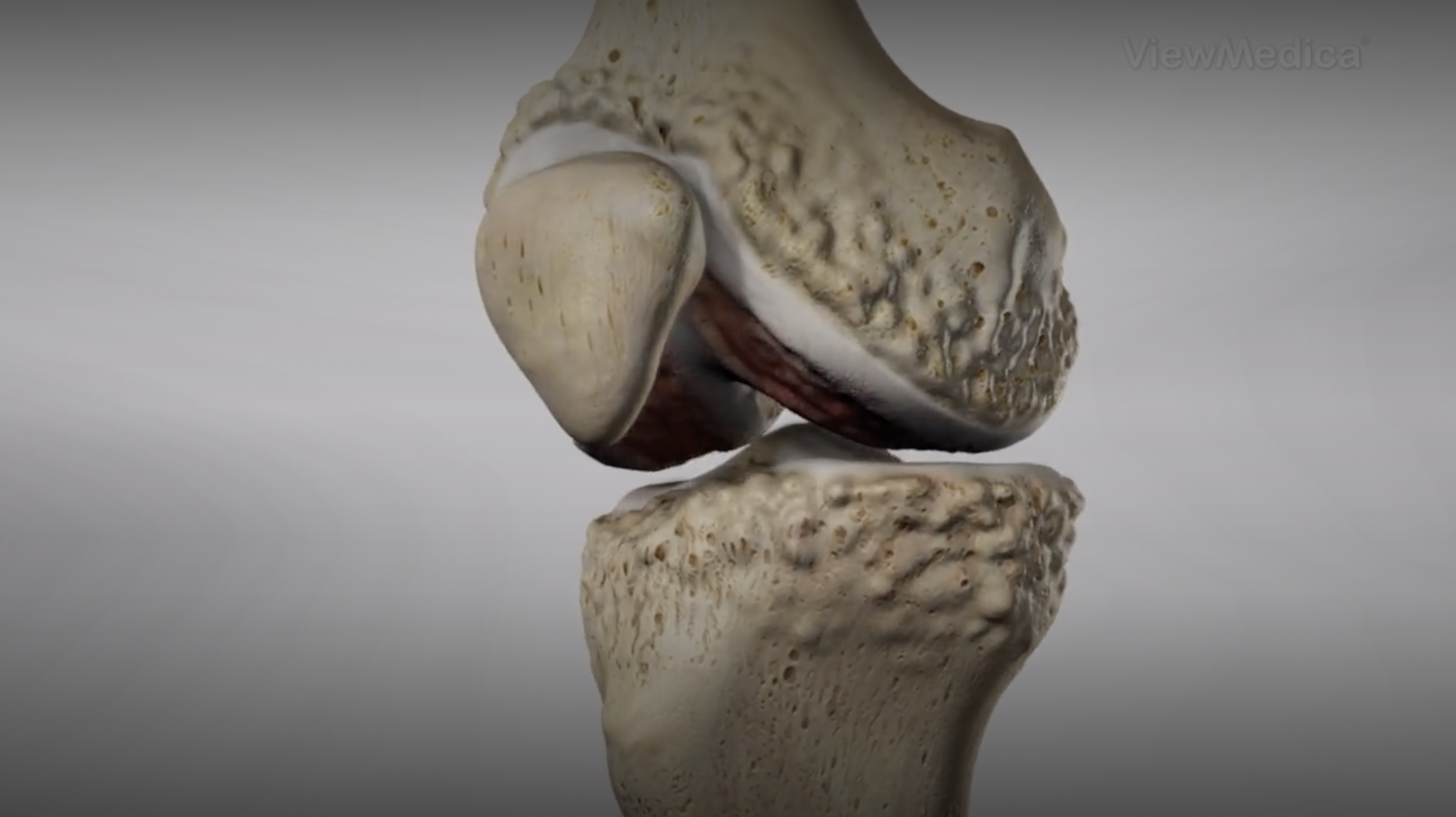
HOW OUR PROVIDERS DIAGNOSE:
1. CONSULTATION
2. PHYSICAL
EXAMINATION
3. CUSTOMIZED
TREATMENT PLAN
CURRENTLY ACCEPTED INSURANCE CARRIERS

Our Patients Love Us
You will not be disappointed
It is always a pleasure coming to SJPS. Everyone is so pleasant and care about your needs. I would and have recommended them to family and friends. You will not be disappointed
- KAI would highly recommend …
My experience with Spine and Joint Pain group has been amazing the procedure on my spine went well and uneventful the procedure was clearly explained and of what to possibly expect from the procedure I would highly recommend them.
- Rena SThe environment was relaxed, pleasant, and professional…
Been going to Spine and Joint for the last few years and my experiences have been positive. Recently had a procedure done and the environment was relaxed, pleasant, and professional. This helps ease some of the stress and edginess that comes with most medical procedures. Thank you S&J.
- AE

